Study Finds 3,625 High-Containment Biolabs Worldwide

The U.S. houses 47% of global BSL-3 facilities — and 91.6% of countries operating them lack dual-use research oversight.
As public discussion around biolabs intensifies following law enforcement’s recent raid of an illicit biolab in Las Vegas, now is a good time to become informed.

Unauthorized “basement biolabs” are undeniably dangerous. But risk is not limited to rogue operators. Government-run and NGO-run high-containment laboratories also handle some of the world’s most dangerous pathogens — and most operate within poorly enforced oversight frameworks.
A newly published global mapping study in the Journal of Public Health provides the most comprehensive count to date of Biosafety Level 3 (BSL-3) and Biosafety Level 4 (BSL-4) laboratories worldwide. The numbers are striking — not just for scale, but for the massive oversight gaps.
THE GLOBAL COUNT
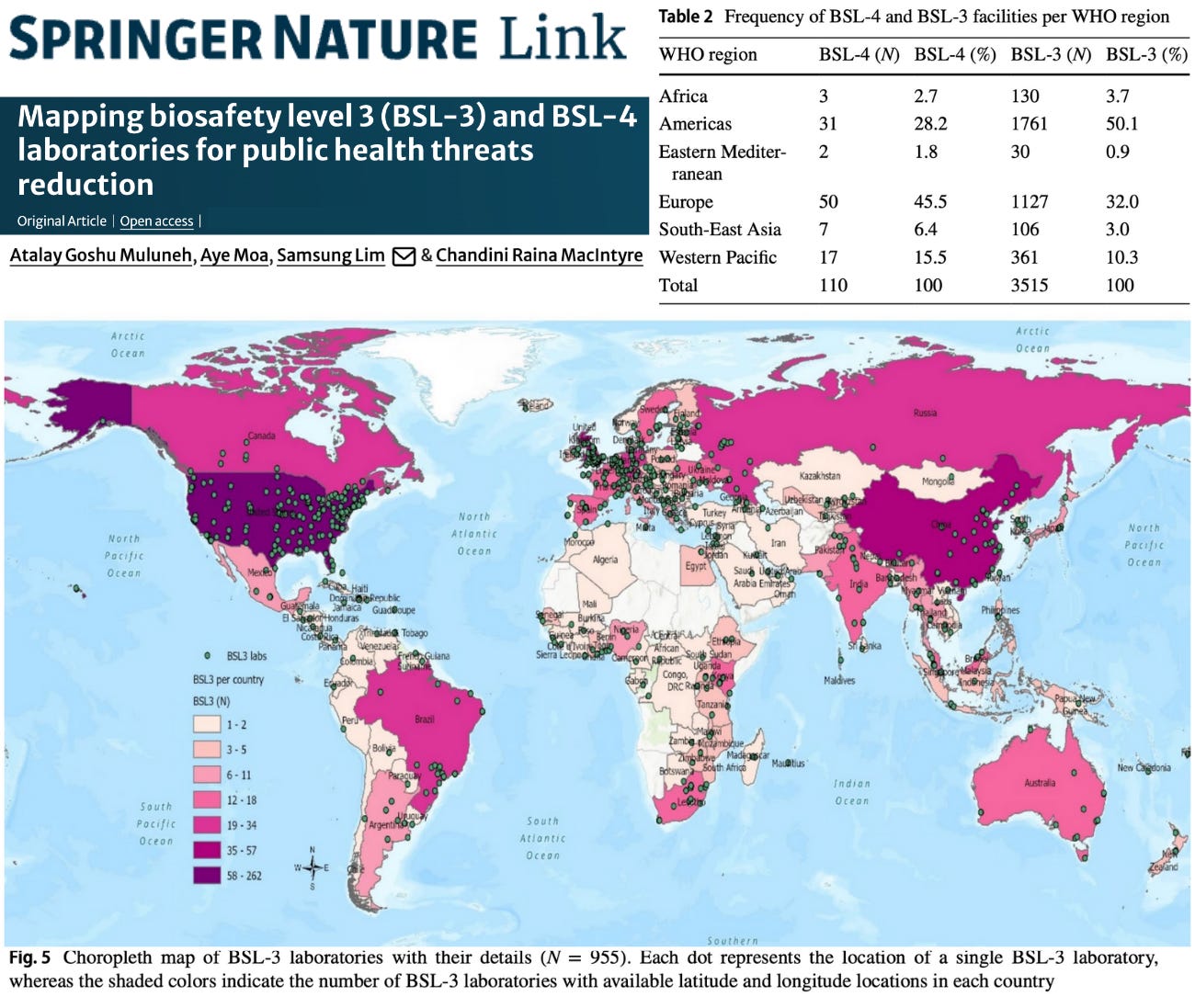
- 3,625 total high-containment labs identified
- 3,515 BSL-3 laboratories
- 110 BSL-4 laboratories
- 149 countries have at least one BSL-3 lab
- 34 countries have at least one BSL-4 lab
This exceeds prior WHO and Global Biolabs estimates, reflecting rapid expansion and incomplete global tracking systems .
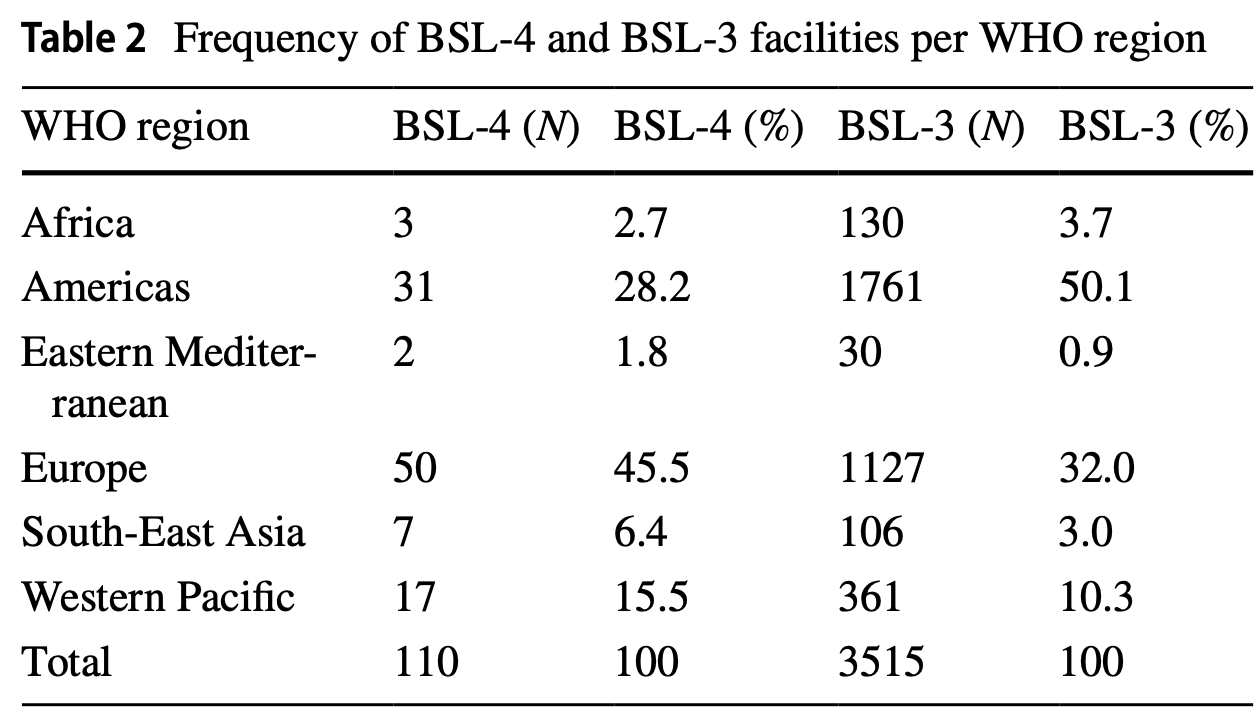
BSL-3 Labs
Together, the US + UK account for nearly two-thirds of all BSL-3 facilities globally. Of the 3,515 BSL-3 labs identified, detailed geolocation and pathogen information was publicly available for only 955 laboratories (~27%). That means roughly 2,500+ labs lack publicly accessible detailed location/pathogen data.
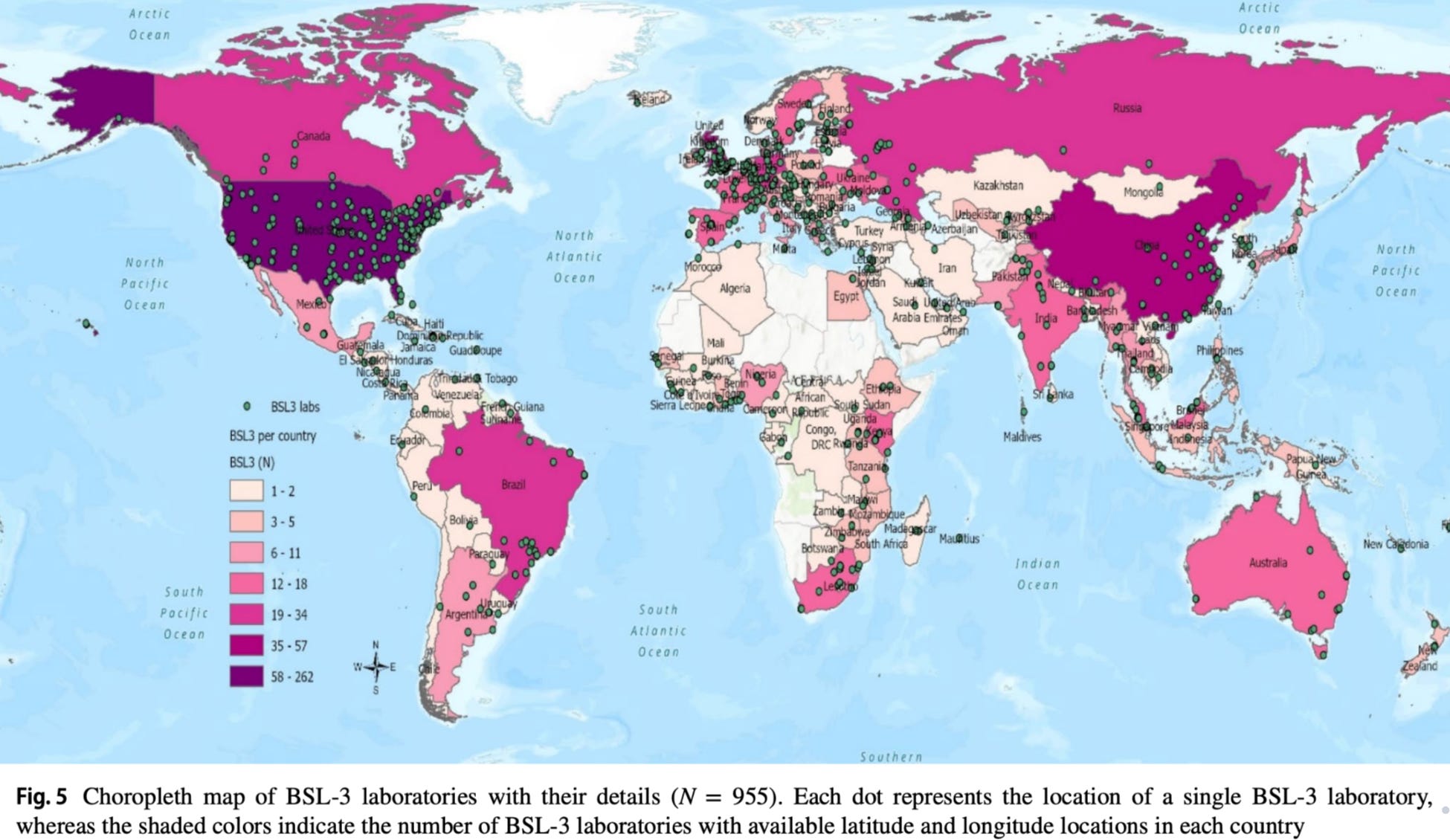
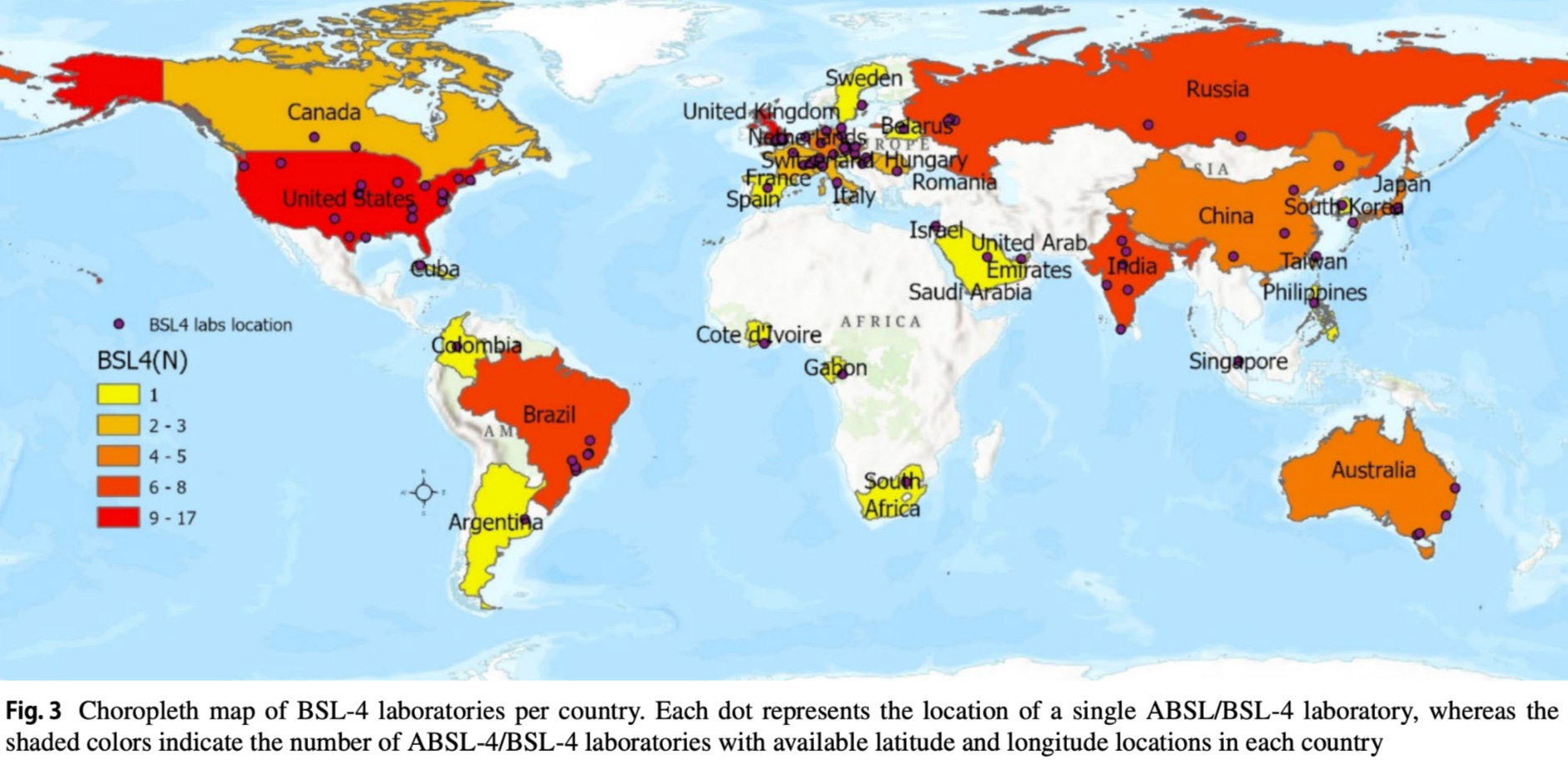
BSL-4 Labs (Highest Containment)
- 17 BSL-4 labs in the United States (highest globally)
- 13 BSL-4 labs in the United Kingdom
- 17 countries have only one BSL-4 lab
OVERSIGHT FAILURE
This is where the findings become most concerning.
Among countries with at least one BSL-3 laboratory, 91.6% (131 of 143 countries) have no guidelines or oversight for dual-use research of concern (DURC) . Only 12 countries (8.39%) report having DURC-related training or formal guidelines.
Dual-use research refers to experiments conducted for legitimate scientific purposes that could also be misused to enhance the danger or functionality of pathogens for nefarious purposes.
DOCUMENTED LAB LEAKS
The study cites prior data documenting 309 laboratory-acquired infections involving 51 different pathogens between 2000 and 2021, including cases that resulted in fatalities .

Yet despite these incidents, there is no comprehensive global registry of high-containment labs, no standardized international oversight mechanism, and no mandatory global reporting framework for dual-use research of concern (DURC) .
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- 3,625 high-containment labs worldwide
- Nearly half of BSL-3 labs in the US alone
- >90% of countries with BSL-3 labs lack dual-use oversight
- Only ~27% of BSL-3 labs have publicly available detailed geolocation data
- No unified global registry exists
The infrastructure handling some of the world’s most dangerous pathogens is expanding — while global oversight remains fragmented, inconsistent, and in many regions virtually absent.
There must be an immediate and complete global moratorium on gain-of-function research, along with comprehensive investigations into the growing number of U.S. and international biolabs—including their funders—that may be conducting bioweapon research, to prevent another man-made pandemic:
https://www.thefocalpoints.com/p/study-finds-3625-high-containment
